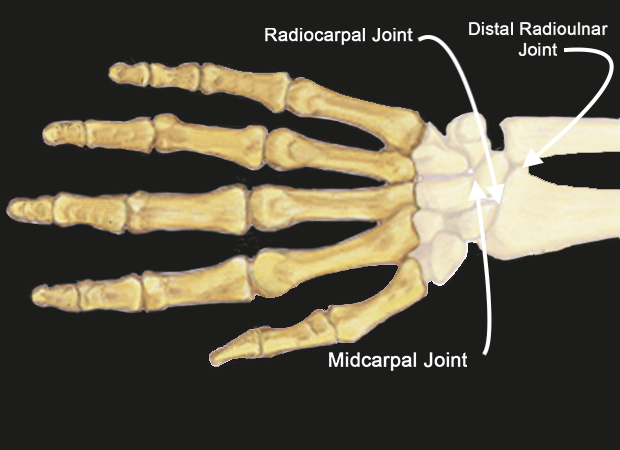
Distal Radioulnar Joint Anatomy
The Distal Radioulnar Joint provides an articulation between:
- Distal End of the Radius
- Ulnar notch
Ligaments:
- Dorsal and Palmar Radioulnar Ligaments
- Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
Joint Type:
- Pivot
- Synovial joint
- Synovial joints are specialized structures that allow movement at bony articulations.
- Composed of a joint cavity lined by synovium containing bones lined with articular cartilage
- Structural components contain:
- Articular cartilage - enables low friction movement
- Ligament
- Joint capsule - Fibrous tissue surrounding joint cavity
- Synovium - Tissue lining non-cartilaginous portions of joint cavity and is composed of two layers, the intimal lining and the connective tissue sublining
- Synovial fluid - Produced and regulated by the synovium
Diagrams & Photos