Juncturae Tendinum Anatomy
Description:
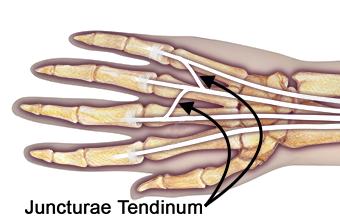
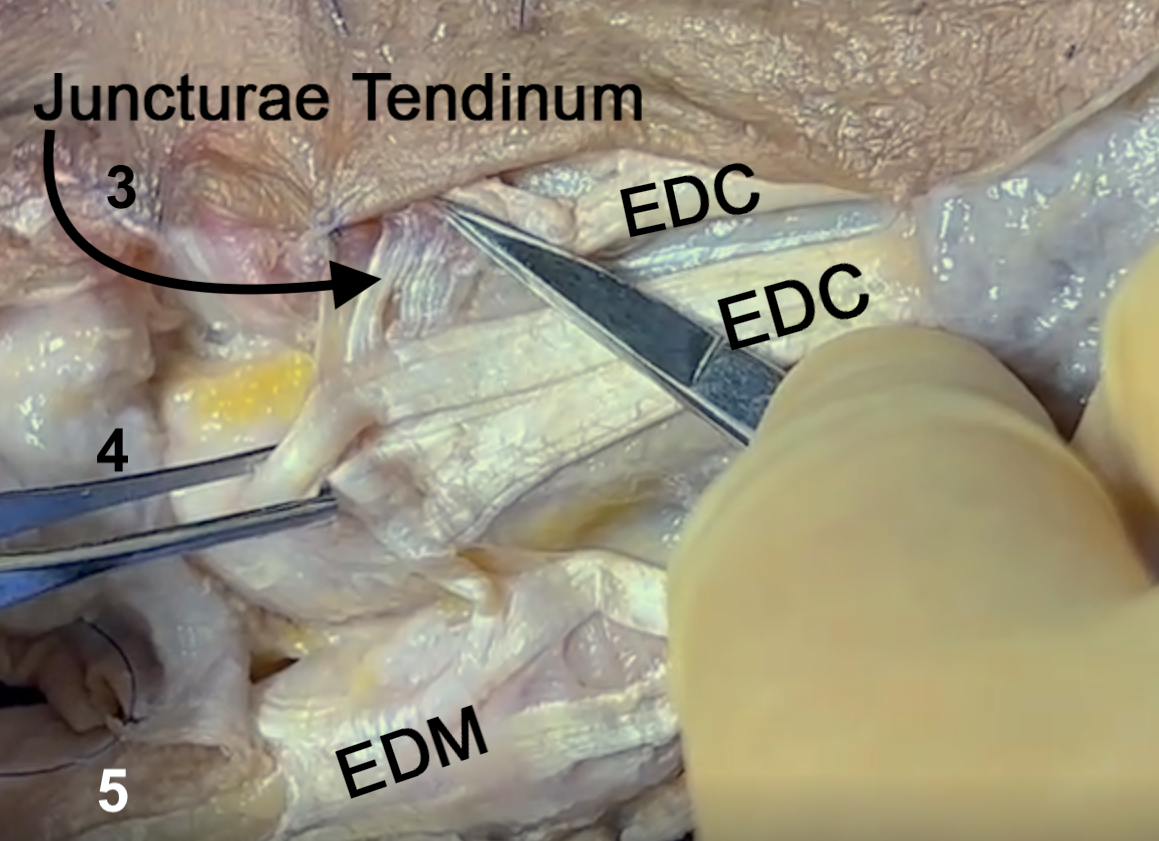
- Juncturae tendinum occur in the intermetacarpal spaces two, three, and four. They are not seen between thumb and index extensors.
- Juncturae tendinum distribute extensor forces, coordinate, and stabilize the extensor digitorum communis slips.
- Juncturae tendinum can mask a laceration of an extensor digitorum communis tendon by providing active extension of the metacarpophalangeal joint when the extensor digitorum communis is actually cut completely.
- Three types of juncturae tendinum have been described. Type I is composed of thin filamentous transverse fibers between slips of the extensor digitorum communis. Type II juncturae tendinum were thicker than Type I. Type II are often rhomboid shaped and oriented obliquely. Type III juncturae tendinum are the thickest and more tendon-like with a "y" or "r" shape.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- Juncturae tendinum do not occur between the thumb and index finger.
- While fascial connections are common between the index and long extensor tendons, juncturae tendinum (Type 3) are rare between the index and long fingers.
- Juncturae tendinum of any type are not always present in the index-long intermetacarpal space (absence 12.5%).
- The juncturae tendinum do not connect to the extensor indicis proprius (EIP).