Median Nerve Anatomy
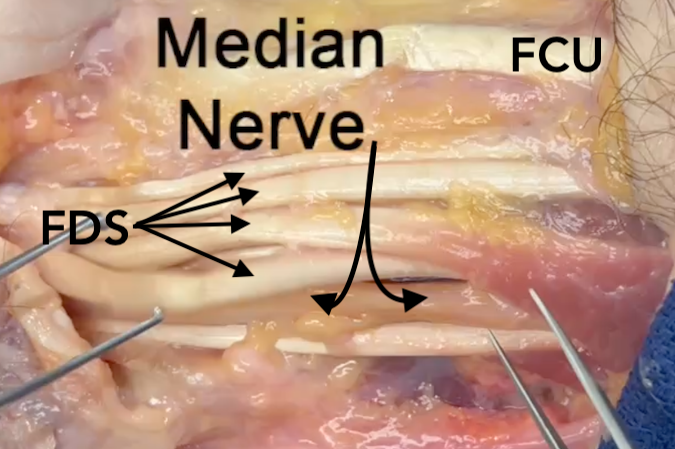
- In section 9 the median nerve accompanied by 11 flexor tendons, the ulnar nerve, the radial artery, and the ulnar artery.
- In the proximal part of section 9 the median nerve is dorsal to the FDS muscle.
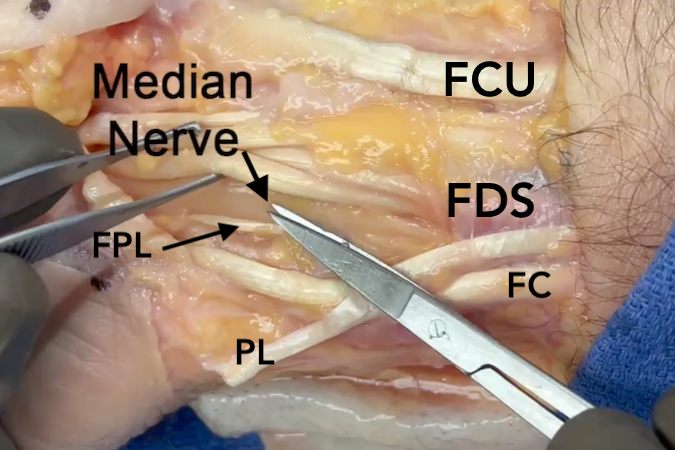
- At the wrist crease the median nerve is dorsal to the palmaris longus.
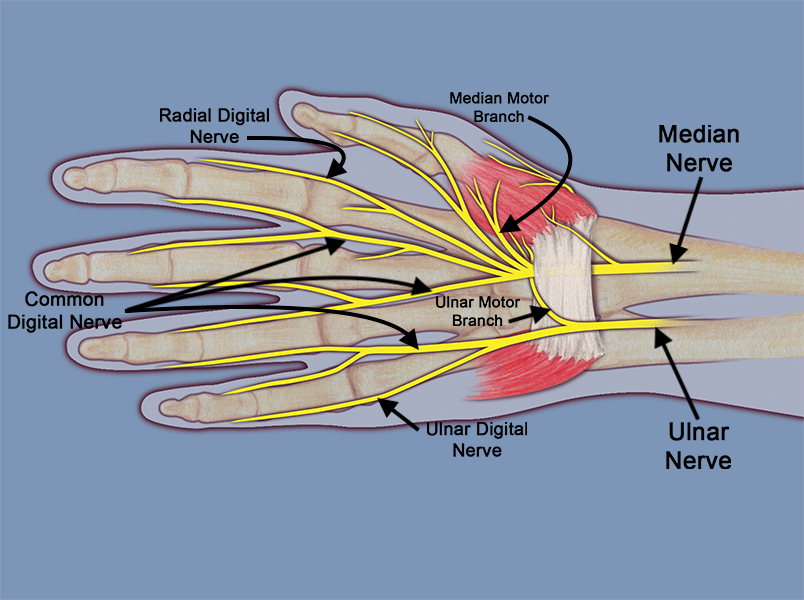
- The common terminal branches of the median nerve are the motor branch to the thenar muscles, the radial and ulnar digital nerves to the thumb, the radial digital nerve to the index, the common digital nerve in the index/long web space, and the common digital nerve in the long/ring web space, and finally the motor nerves to the first two lumbrical muscles.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- In Section 9 the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve originates from the radial edge of the median nerve approximately 6 cm. proximal to the wrist flexion crease.
- The median nerve is positioned volar radially in the carpal tunnel dorsal to the palmar fascia and transverse carpal ligament.
- The radial side of the carpal tunnel is formed by the distal scaphoid and the trapezial ridge. The dorsal part is formed by the scaphoid, lunate, capitate, and hamate. The ulnar side is formed by the hook of hamate and pisiform.
- The motor branches to the first two lumbrical muscles are branches of the index radial digital nerve and index/long common digital nerve.