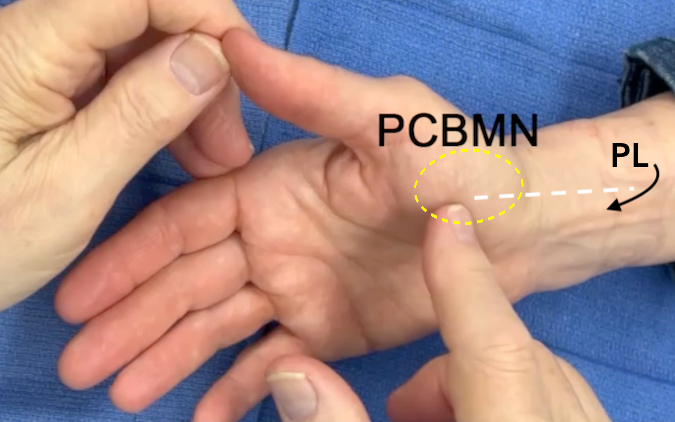
Palmar Cutaneous Branch of the Median Nerve
- To assess the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve. Examine the sensation in the base of the thenar eminence.
- Always compare the sensory findings to the opposite uninjured side.
- Check for scars along the course of the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve.
- Check for a positive Tinel’s sign along the course of the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve’
- Symptoms from a palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve neuroma can be aggravated by wrist motion, especially dorsiflexion.
- Neuroma pain weakens grip strength.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve is subject to iatrogenic injury during carpal tunnel release or any surgery in the section 9 area between the distal palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis.
- Injury to the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve can cause a neuroma with resultant pain, paresthesias, and numbness in the base of the thenar eminence.