Radial and Ulnar Digital Arteries Index, Long, Ring and Little and Vein Anatomy
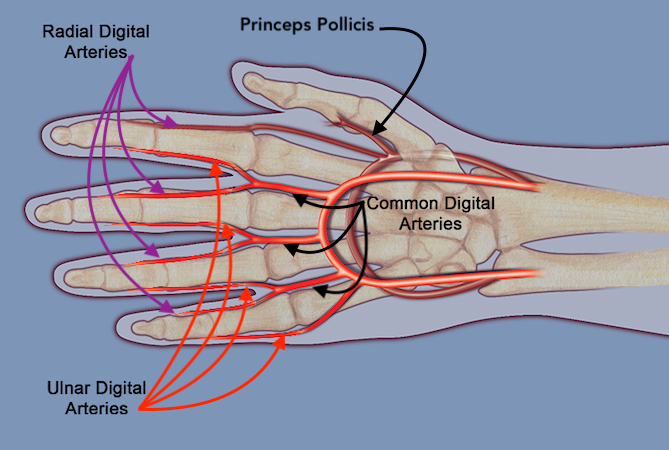
- The palmar digital arteries of the fingers originate from the bifurcation of the common digital arteries.
- In the fingers the neurovascular bundles are supported by the Grayson’s and Cleland’s ligaments which are primarily located between the MP, PIP, and DIP joints.
- The palmar digital arteries of the fingers communicate with each other by transverse digital arches.
- The palmar digital arteries of the fingers send vessels through the short and long vincula to provide blood supply to the FDP and FDS tendons.
- The smallest arteries in the hand are the ulnar digital artery of the little, radial digital artery of the index, and radial digital artery of the thumb.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
Arteries:
- The radial digital artery of the index along with the princeps pollicis are both terminal branches of dorsal part of the radial artery.
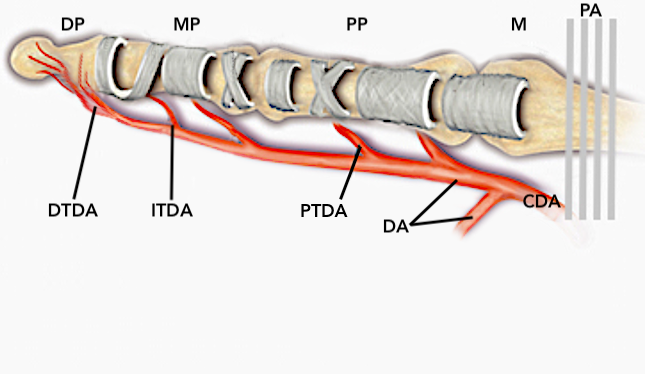
- The proximal, middle (intermediate), and distal transverse digital arches provide arterial connections between the radial and ulnar digital arteries.
- The middle (intermediate) and distal transverse digital arches are located near the C1 and C2 pulleys respectively.
- The proximal, middle (intermediate), and distal transverse digital arches are dorsal to the flexor tendons.
Veins:
- The palmar digits are drained by a superficial and deep venous system.
- Digital vena comitantes have a variable presence in this venous drainage system.
- Palmar (volar) digital veins connected to dorsal veins by oblique intercapitular or communicating veins thar drain into veins of the dorsal finger, hand, and wrist.