Ulnar Nerve in Guyon's Canal
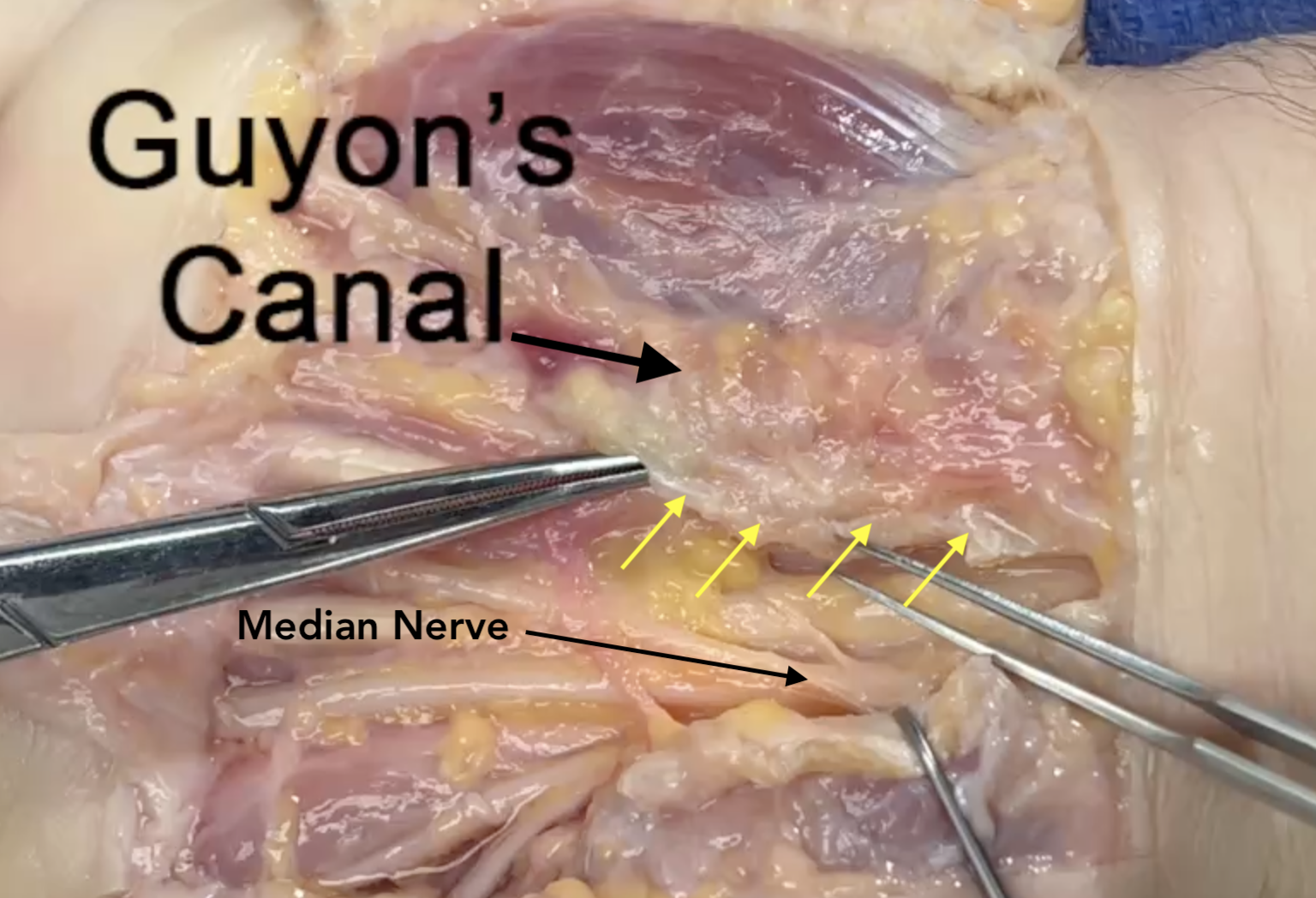
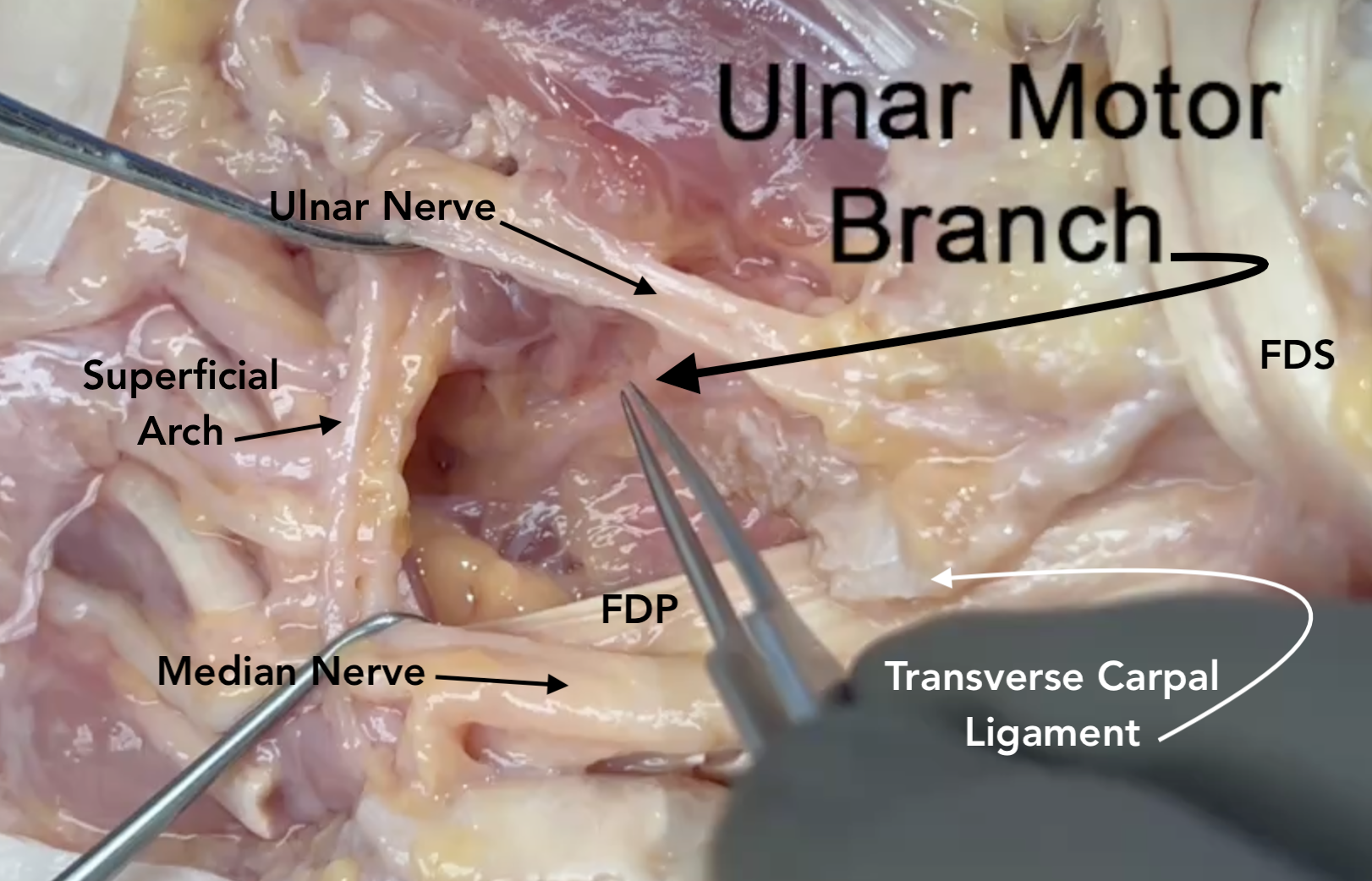
- In Section 8 the ulnar nerve is located in Guyon’s Canal with the ulnar artery.
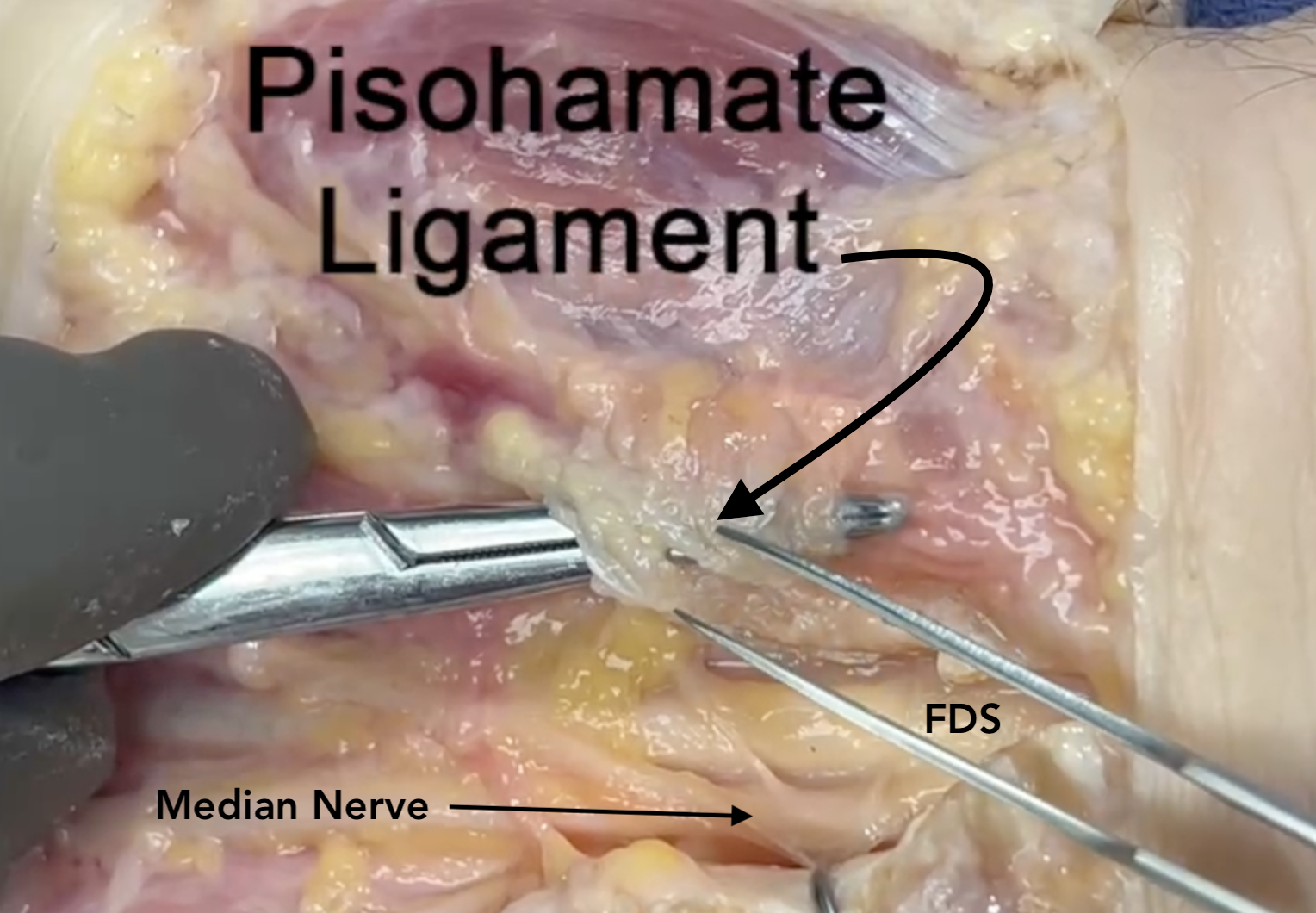
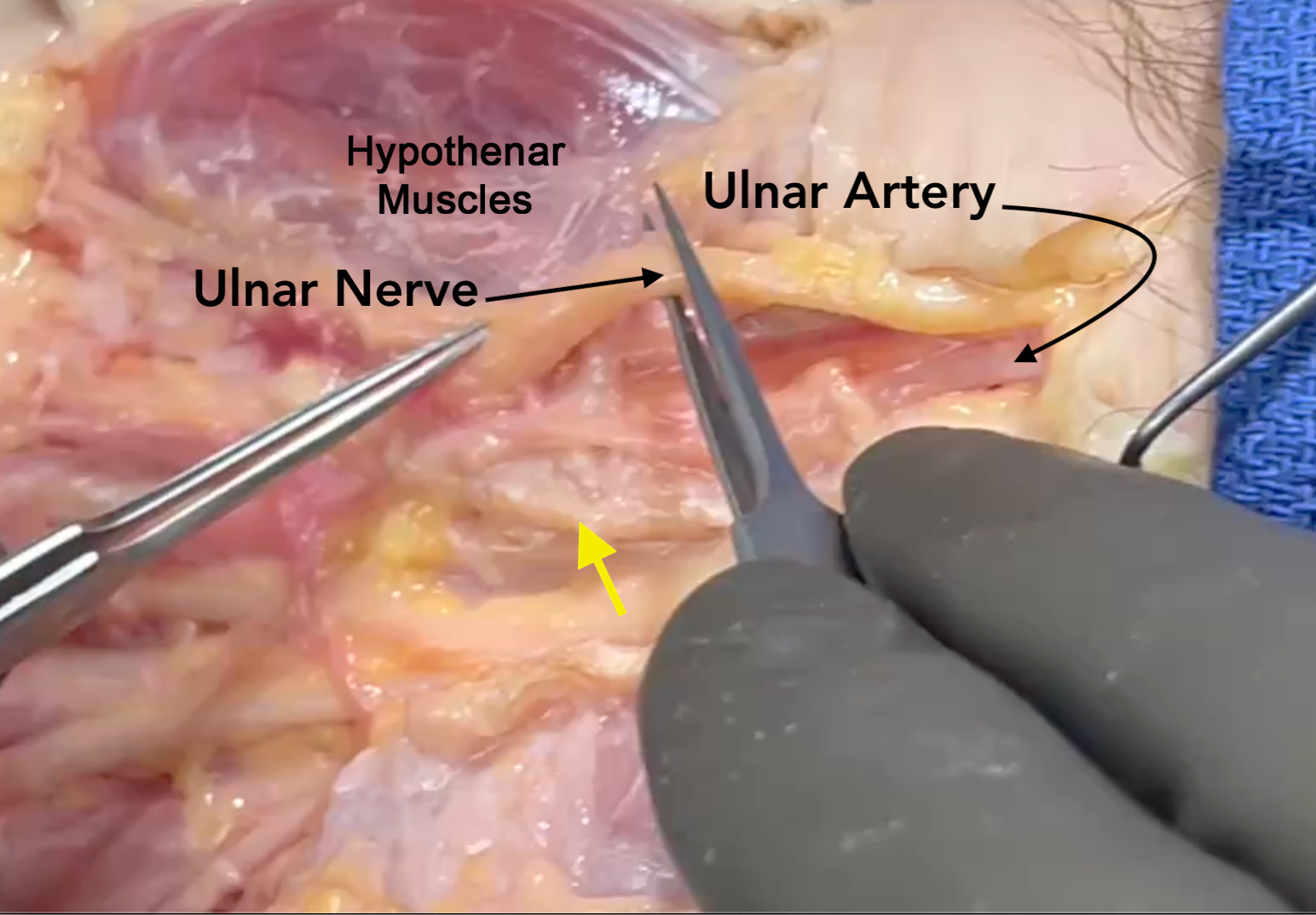
- The ulnar nerve is positioned volar and superficial to the ulnar artery in Guyon’s Canal dorsal to the pisohamate ligament.
- Proximally the ulnar nerve is radial to the pisiform and FCU tendon muscle.
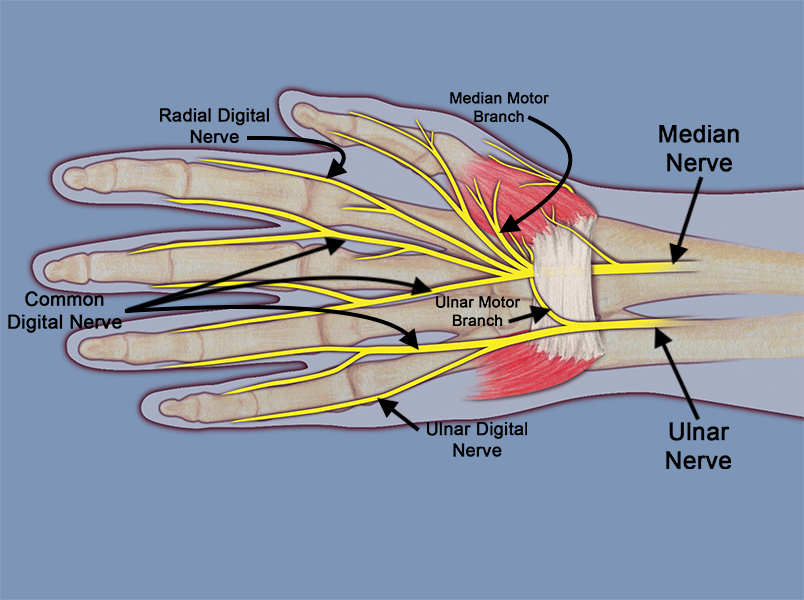
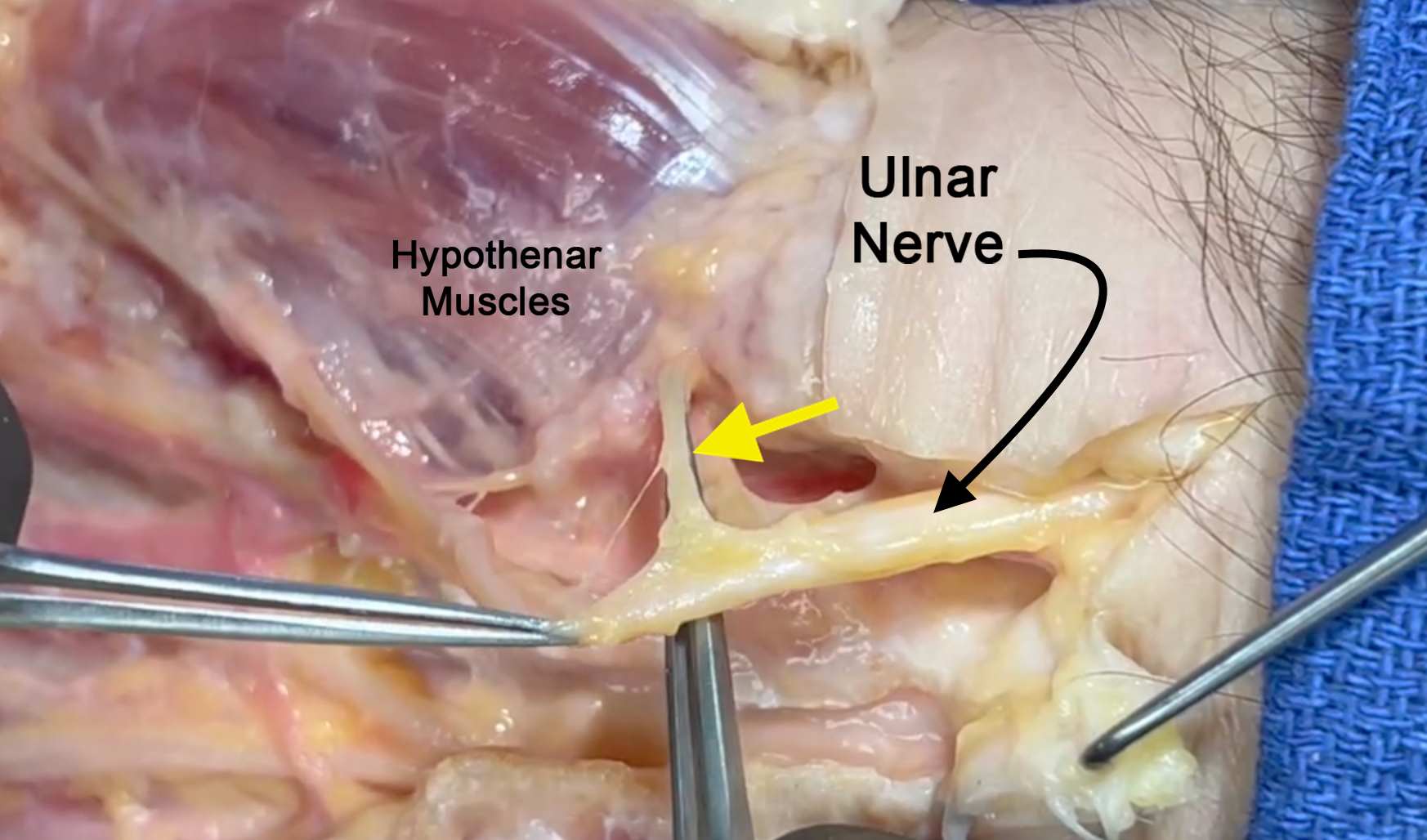
- The common terminal branches of the ulnar nerve are the deep motor branch to the adductor pollicis and deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis muscles, motor branch to the hypothenar muscles and the ulnar two lumbricals, the ulnar digital sensory nerve to the little finger, and the common digital sensory nerve in the ring/little web space.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- The ulnar nerve originates from the medial cord of the brachial plexus, specifically from the C8-T1 nerve roots.
- The ulnar nerve also provides motor innervation to the ulnar innervated intrinsic muscles which include the hypothenar muscles, the dorsal and volar interosseous muscles, the ulnar two lumbrical muscles, the adductor pollicis, and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis are all innervated by the ulnar nerve.
- The proximal third of Guyon’s Canal contains motor and sensory components of the ulnar nerve so compressing lesions can affect motor and sensory function, the middle third motor and sensory separate and lesions compressing the nerve typically affect the motor branch, and in the distal third only sensory parts are at risk for compression.
- Potential compressive lesions include ganglions, lipoma, hemangiomas, ulnar artery thrombosis or ulnar artery aneurysms.