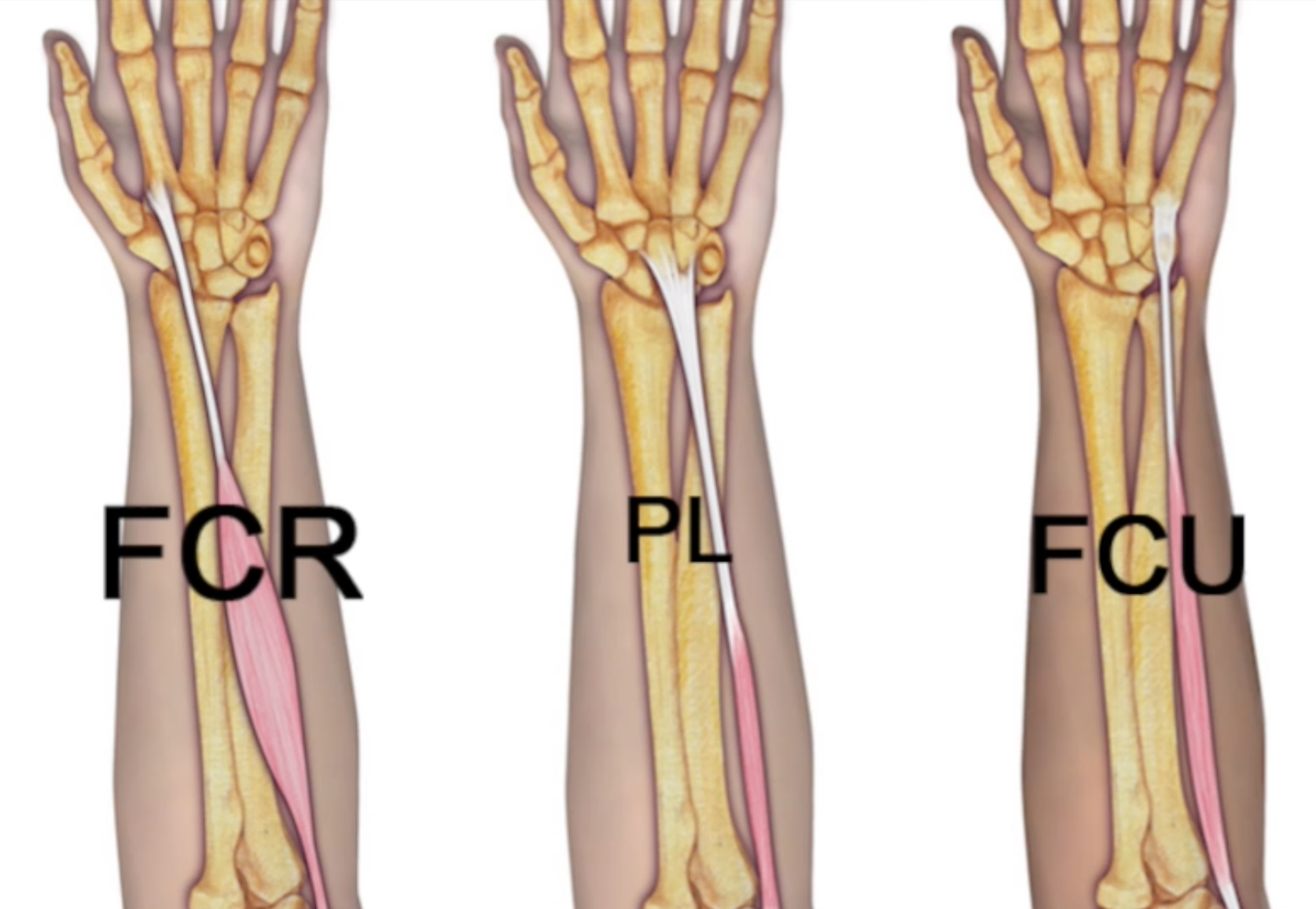
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
- Origin: Humeral head: Humerus (medial epicondyle via common flexor tendon)
Ulnar head: Ulna (olecranon, medial margin; shaft, proximal 2/3 posterior via an aponeurosis)
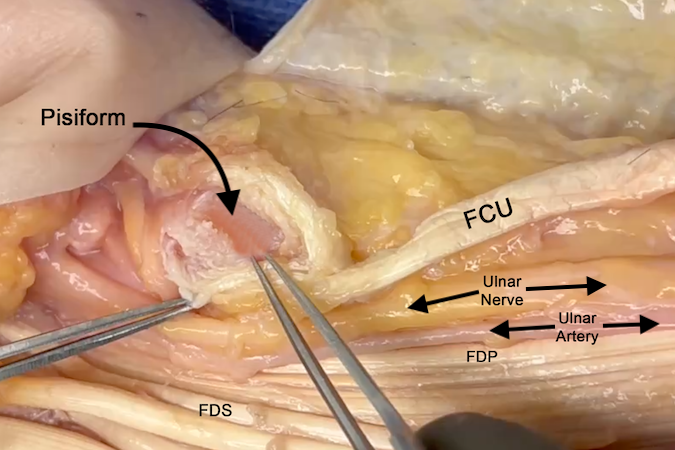
Intermuscular septum - Insertion: Pisiform
Hamate
5th metacarpal, base
Flexor retinaculum - Innervation: Cervical roots): C7-T1
Nerve: ulnar nerve - At distal volar wrist crease the ulnar artery and nerve are radial to the FCU tendon.
- The FCU muscle has two heads. The ulnar nerve can be entrapped proximally between the two heads.
- The FCU muscle tendon unit is in the superficial group of volar forearm muscles.
- The FCU muscle is the only volar forearm muscle completely and only innervated by the ulnar nerve.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) muscle is the most powerful wrist flexor.
- The pisiform is a sesamoid-like bone surrounded by the FCU tendon.
- The pisiform forms the ulnar side of Guyon’s canal.
- There is internervous plane between the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) and the extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) which provides a safe route for ulnar shaft exposure during ORIF of ulnar fractures.
- The dorsal ulnar sensory nerve passes through or just distal to the FCU muscle as it travels to the dorsum of the ulnar wrist and hand.