Ulnar Nerve
- In patients with lacerations, sensation is assessed by examining light touch and/or two-point discrimination.
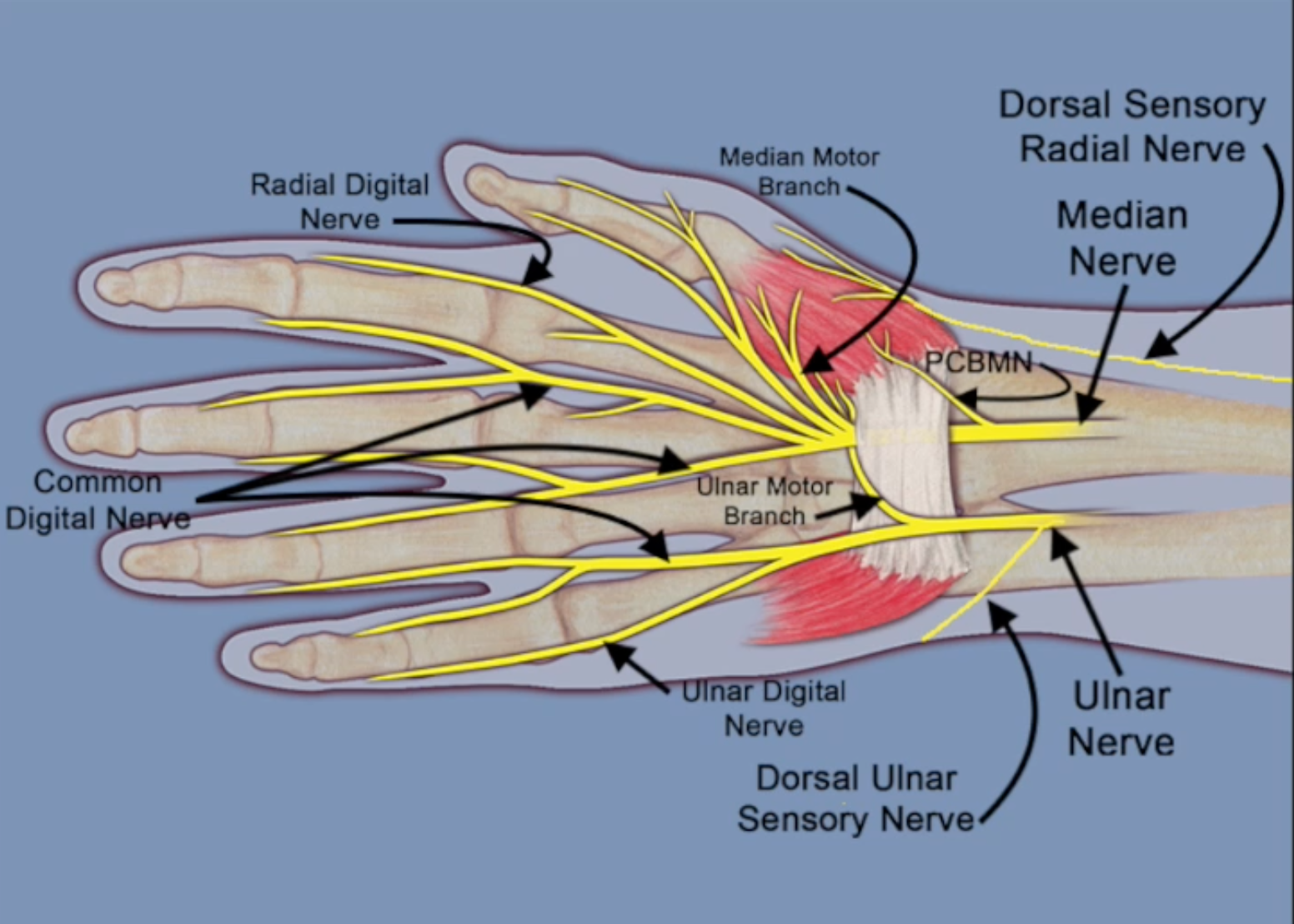
- The ulnar nerve provides sensation palmarly to the little finger and ulnar half of the ring finger.
- The ulnar nerve also supplies the dorsal sensation around the fingernail and dorsal DIP joint of the ring and little fingers. This sensation is supplied by the dorsal branches of the digital nerves which originates from the ulnar nerve.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- The dorsal ulnar sensory nerve passes through or just distal to the FCU muscle at a point 7-8 cm proximal to the ulnar styloid before going to the dorsal ulnar wrist and hand.
- At the wrist level there is a consistent fascicular pattern of the ulnar nerve branches with the main ulnar nerve trunk. The radial most fascicular group is the volar sensory fibers, and the most ulnar group is the dorsal sensory branch of the ulnar nerve.
- The fascicular groups in the distal ulnar nerve facilitate nerve transfers between the AIN and the motor branches of the ulnar nerve.
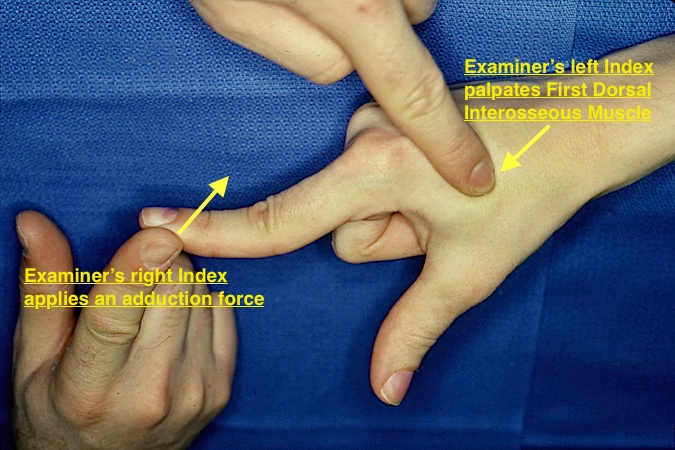
- Potential compressive lesions include ganglions, lipoma, hemangiomas, ulnar artery thrombosis or ulnar artery aneurysms.