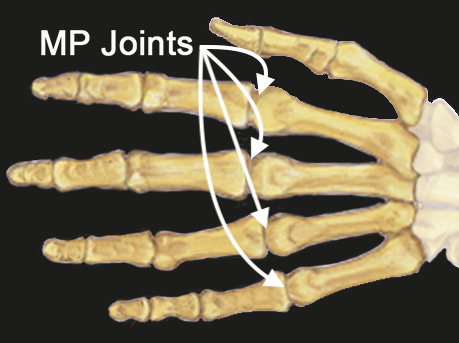
MP Joints Index, Long, Ring and Little Anatomy
The MP Joint provides an articulation between metacarpal and proximal phalanges:
- Metacarpal Bone: The long bone within the hand that extends from the distal carpal row to the base of the fingers.
- Proximal Phalanx: The first bone of the finger, located between the MP joint and the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint.
Ligaments:
- Collateral Ligaments: These ligaments provide side-to-side stability, preventing excessive lateral movement.
- Volar plate which limits MP joint hypertension.
Joint Type:
- Condyloid
- Synovial joint
- Synovial joints are specialized structures that allow movement at bony articulations.
- Composed of a joint cavity lined by synovium containing bones lined with articular cartilage
- Structural components contain:
- Articular cartilage - enables low friction movement
- Ligaments for joint stability
- Joint capsule - Fibrous tissue surrounding joint cavity. Note collateral ligaments are part of the capsule.
- Synovium - Tissue lining non-cartilaginous portions of joint cavity. Synovium is composed of two layers, the intimal lining and the connective tissue sublining
- Synovial fluid - joint lubricant produced and regulated by the synovium
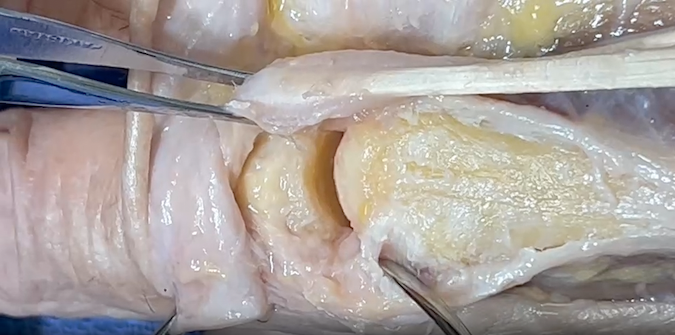
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- Most MP dislocations are simple, meaning there is no soft tissue interposed in the joint.
- Simple dislocations can usually be reduced by closed reduction.
- Complex dislocations occur far less frequently but require surgical intervention in most cases because the dislocation can not be reduced unitl the interposed tissue is surgically removed from the joint.