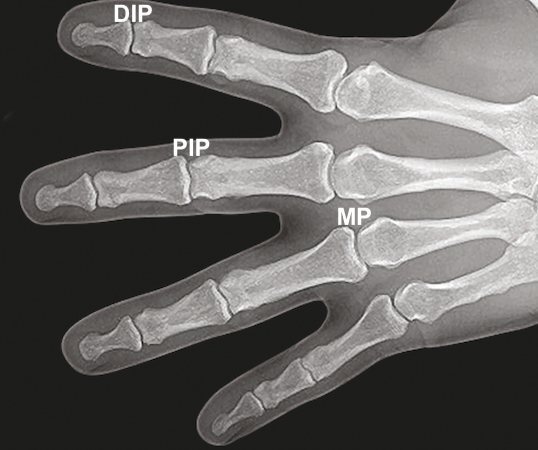
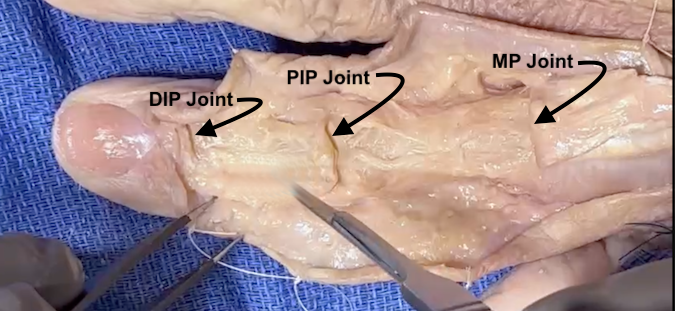
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Anatomy
The DIP Joint provides an articulation between:
- Middle Phalanx
- Distal Phalanx
Ligaments:
- Collateral Ligaments: Provide side-to-side stability.
Tendons crossing the DIP Joint:
- Flexor Digitorum Profundus (FDP)
- Extensor Digitorum
IP joint type:
- Hinge joint
- Synovial joint
- Synovial joints are specialized structures that allow movement at bony articulations.
- Composed of a joint cavity lined by synovium containing bones lined with articular cartilage
- Structural components contain:
- Articular cartilage - enables low friction movement
- Ligaments
- Joint capsule - Fibrous tissue surrounding joint cavity
- Synovium - Tissue lining non-cartilaginous portions of joint cavity and is composed of two layers, the intimal lining and the connective tissue sublining
- Synovial fluid - Joint lubricant produced and regulated by the synovium
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- Common problems at this joint include Mallet Finger