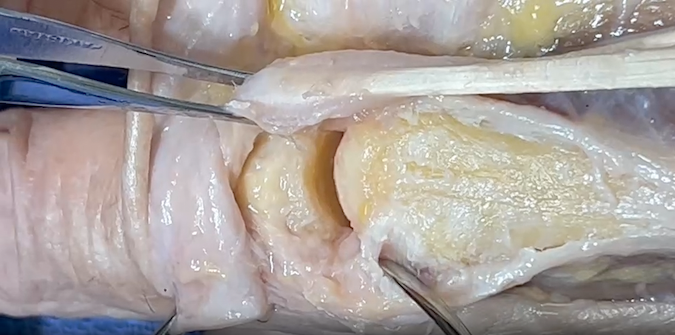
Metacarpal Phalangeal (MP) Joint Anatomy
The MP Joint provides an articulation between:
- Metacarpal Bone: The long bone within the hand that extends from the wrist to the base of the fingers.
- Proximal Phalanx: The first bone of the finger, located between the MP joint and the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint.
Ligaments:
- Collateral Ligaments: These ligaments provide side-to-side stability, preventing excessive lateral movement.
- Extensor Digitorum: Extends the MP joint.
Joint Type:
- Condyloid
- Synovial joint
- Synovial joints are specialized structures that allow movement at bony articulations.
- Composed of a joint cavity lined by synovium containing bones lined with articular cartilage
- Structural components contain:
- Articular cartilage - enables low friction movement
- Ligament
- Joint capsule - Fibrous tissue surrounding joint cavity
- Synovium - Tissue lining non-cartilaginous portions of joint cavity and is composed of two layers, the intimal lining and the connective tissue sublining
- Synovial fluid - Produced and regulated by the synovium
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- Most MP dislocations are simple, meaning there is no soft tissue within the joint and the injury can usually be reduced by closed reduction, while complex dislocations occur far less frequently but require surgical intervention in most cases.